In today’s connected world, encountering Wi-Fi connection problems can bring your digital life to a frustrating halt. Whether you’re trying to join a home network, access public Wi-Fi, or troubleshoot persistent connectivity issues, this comprehensive guide will help you diagnose and resolve Wi-Fi sign-in problems quickly and effectively.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Wi-Fi Connection Problems
Before diving into solutions, it’s essential to understand what might be preventing your connection in the first place. Wi-Fi connectivity issues stem from various sources, and identifying the root cause is your first step toward resolving them.
Common Reasons Why Wi-Fi Networks Won’t Connect
Wi-Fi connection failures typically fall into several categories:
- Signal strength issues: When your device is too far from the router or there are physical barriers blocking the signal
- Authentication problems: Incorrect passwords or authentication protocols that don’t match between your device and the network
- Router/modem malfunctions: Hardware issues affecting your network equipment
- Device compatibility issues: Outdated drivers or software incompatible with certain network types
- Network overload: Too many devices competing for bandwidth on the same network

Understanding which category your problem falls into can save you time and frustration during troubleshooting.
How Wi-Fi Networks Really Work
Wi-Fi connectivity isn’t as simple as it seems. A successful connection requires several stages to complete properly:
- Discovery phase: Your device scans for available networks using radio signals
- Authentication: Your device presents credentials (like a password) to gain access
- IP assignment: Once authenticated, your device receives an IP address through DHCP
- DNS resolution: Your device needs to translate domain names into IP addresses
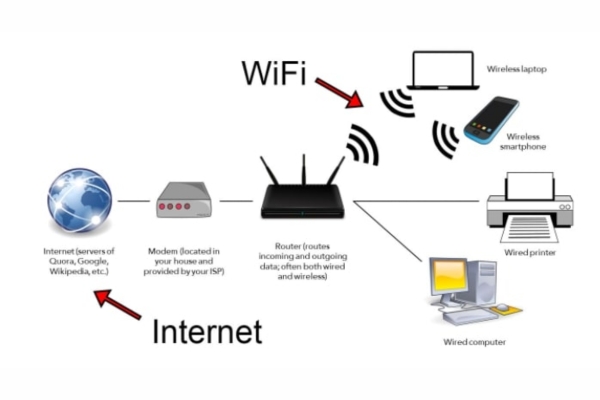
A failure at any of these stages can prevent you from connecting successfully. Most device error messages correspond to a specific stage in this process, providing clues about what’s going wrong.
Identifying Your Specific Wi-Fi Problem
Before attempting fixes, determine exactly what type of issue you’re facing:
- Can’t see the network: Your device doesn’t detect the Wi-Fi network at all
- Can’t connect to the network: You see the network but can’t join it successfully
- Connected but no internet: Your device connects to the Wi-Fi but can’t access the internet
- Intermittent connectivity: Your connection drops randomly or works inconsistently
Most operating systems offer diagnostic tools that can help pinpoint the issue. Look for network troubleshooters in your device settings, and pay attention to specific error messages, which often contain valuable information about what’s going wrong.
Immediate Solutions for Common Wi-Fi Sign-in Problems
Once you’ve identified the general nature of your issue, try these proven solutions that resolve most common Wi-Fi sign-in problems.
Fix 1: Restart Your Device and Router (The Power Cycle Method)
This simple yet effective approach resolves a surprising number of connectivity issues:
- Power down your device completely (not just sleep mode)
- Unplug your router and modem from power
- Wait 30 seconds to ensure all capacitors discharge
- Plug the modem back in first and wait for it to fully initialize (usually 1-2 minutes)
- Connect the router next and wait for all lights to stabilize
- Turn your device back on and attempt to connect

This process resets network configurations and clears temporary memory issues that might be interfering with your connection.
Fix 2: Forget and Reconnect to the Network
If you can see the network but can’t connect successfully, try removing it from your saved networks and starting fresh:
On Windows:
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi
- Select “Manage known networks”
- Find your network, select it, and click “Forget”
- Reconnect by selecting the network from the available list and entering the password again
On Android:
- Go to Settings > Connections > Wi-Fi
- Long-press the problematic network
- Select “Forget network”
- Reconnect with fresh credentials
On iOS/macOS:
- Go to Settings > Wi-Fi (iOS) or click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar (macOS)
- Find your network and select “Forget This Network”
- Reconnect by selecting it again and entering the password
This process clears potentially corrupted network settings and cached credentials that might be causing authentication problems.
Fix 3: Check Your Password and Authentication Settings
Authentication failures are among the most common connection issues:
- Verify your password: Double-check for typos, case sensitivity, and special characters
- Check authentication type: Ensure your device supports the network’s security protocol (WPA2, WPA3, etc.)
- Toggle airplane mode: On mobile devices, turning airplane mode on and off can reset network adapters
- Check for MAC filtering: Some networks restrict access to specific devices; contact the network administrator if you suspect this is the issue
Remember that some routers have a physical reset button that can be used if you’ve forgotten the password, though this will reset all router settings.
Device-Specific Troubleshooting Guides
Different devices require different approaches when troubleshooting Wi-Fi connection problems.
Solving Wi-Fi Sign-in Problems on Windows Devices
Windows offers several built-in tools to diagnose and fix network issues:
- Windows Network Diagnostics: Right-click on the Wi-Fi icon in the taskbar and select “Troubleshoot problems”
- Command prompt solutions:
ipconfig /releasefollowed byipconfig /renewto request a new IP addressipconfig /flushdnsto clear the DNS cachenetsh winsock resetto reset Winsock (Windows’ network programming interface)
- Update network drivers: Search for “Device Manager,” expand “Network adapters,” right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, and select “Update driver”
- Reset network stack: In Windows 10/11, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network reset
These tools can resolve most Windows-specific networking issues by refreshing system components that handle Wi-Fi connections.
Fixing Wi-Fi Connection Issues on Mac and iOS
Apple devices have their own set of troubleshooting options:
- macOS Wireless Diagnostics: Hold Option and click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar, then select “Wireless Diagnostics”
- Create a new network location:
- Go to System Preferences > Network
- Click the Location dropdown and select “Edit Locations”
- Click the “+” button to create a new location
- Configure your Wi-Fi settings from scratch
- Reset PRAM/NVRAM: Restart your Mac and immediately hold Option+Command+P+R until you hear the startup sound twice
- iOS network settings reset: Go to Settings > General > Reset > Reset Network Settings (note: this will remove all saved Wi-Fi passwords)
These Apple-specific fixes address the unique way macOS and iOS handle network configurations.
Android Wi-Fi Troubleshooting Steps
Android devices offer several troubleshooting options:
- Reset network settings: Go to Settings > System > Reset options > Reset Wi-Fi, mobile & Bluetooth
- Boot in safe mode: Hold the power button, then press and hold “Power off” until “Safe mode” appears
- Check manufacturer-specific issues: Some Android devices have known Wi-Fi bugs that require specific fixes or firmware updates
- Clear network settings provider data: Go to Settings > Apps > See all apps > Show system > “Com.android.providers.settings” > Storage > Clear data
Android’s diverse ecosystem means some issues might be specific to your device manufacturer, so check their support pages for device-specific guidance.
Smart Device Wi-Fi Connection Solutions
Other internet-connected devices require different approaches:
- Smart TVs:
- Ensure your TV’s firmware is updated
- Position your TV closer to the router if possible
- Use an Ethernet connection if Wi-Fi is unreliable
- Gaming consoles:
- Set a static IP address in your console’s network settings
- Forward necessary ports on your router for gaming services
- Consider using a wired connection for more stable gameplay

- IoT devices (smart home products):
- Ensure they support your Wi-Fi security type (some only work with 2.4GHz networks)
- Use the manufacturer’s app for troubleshooting
- Position these devices within good range of your router
These devices often have limited user interfaces, making troubleshooting more challenging but still possible with the right approach.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
When basic solutions don’t work, it’s time to explore more advanced troubleshooting methods.
Router Configuration Fixes
Your router settings might need adjustment:
- Access router settings: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address (typically 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1)
- Update router firmware: Check for and install any available updates
- Adjust wireless settings:
- Change the wireless channel to avoid interference
- Set bandwidth settings appropriately (20MHz for better range, 40MHz+ for better speed)
- Make sure DHCP is enabled for automatic IP assignment
- Factory reset the router: Use the physical reset button (usually a small pinhole) as a last resort

Remember to document your important settings before making significant changes or performing a factory reset.
Network Signal Optimization
Sometimes the issue is simply poor signal quality:
- Optimal router placement:
- Position it centrally in your home
- Elevate it off the floor
- Keep it away from metal objects and electronic devices
- Avoid thick walls and appliances like microwaves
- Reducing interference:
- Switch to 5GHz if there’s congestion on 2.4GHz
- Turn off nearby Bluetooth devices
- Change your microwave if it operates on the same frequency
- Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app: These tools show channel congestion and signal strength to help you select the best channel
Improving signal quality can resolve connection issues where the problem isn’t the authentication but the quality of the connection itself.
Addressing IP Address Conflicts and DHCP Issues
Network addressing problems can prevent successful connections:
- Check for IP conflicts:
- Use the command
ipconfig /all(Windows) orifconfig(Mac/Linux) to view your IP configuration - If you see “IP conflict” errors, your device may have the same IP as another device
- Use the command
- Set a static IP address:
- Note your current IP, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS servers
- Go to your device’s network settings
- Switch from DHCP (automatic) to static/manual
- Enter the information you noted, but change the last digit of the IP
- Expand DHCP pool: If your router has limited IP addresses available, increase the range in router settings
These adjustments help resolve addressing issues that prevent proper network communication.
Using Network Analysis Tools
Professional tools can provide deeper insights:
- Wi-Fi analyzer apps: Applications like WiFi Analyzer (Android) or NetSpot (Windows/Mac) visualize your wireless environment
- Ping and traceroute: Use these command-line tools to test connectivity to specific destinations
- Wireshark: This advanced tool can capture and analyze network traffic to identify specific connection issues
These tools help identify problems that aren’t immediately obvious through standard troubleshooting.
Specific Solutions for Public Wi-Fi Challenges
Public Wi-Fi networks present unique challenges that require specific approaches.
Troubleshooting Hotel and Airport Wi-Fi Connections
Hospitality and transportation Wi-Fi networks often have special requirements:
- Clear browser cache and cookies: Previous sessions might interfere with authentication
- Check time limits: Many networks disconnect after a certain period; reconnecting may require re-authentication
- Request login information: Front desk or information booth staff can provide current access credentials
- Connect multiple devices: Some networks limit connections per room or ticket; ask about options for additional devices
- MAC address registration: Some systems require registering your device’s MAC address with the front desk

Understanding these special requirements can save time when dealing with commercial Wi-Fi systems.
Connecting to Coffee Shop and Restaurant Networks
Retail establishment networks have their own quirks:
- Look for network information: Check receipts, signs, or ask staff for the correct network name and password
- Handle click-through agreements: Some networks require accepting terms of service; open your browser after connecting to find these pages
- Refresh captive portals: If a login page doesn’t load, try entering “captive.apple.com” or “connectivitycheck.gstatic.com” in your browser
- Deal with timed sessions: Some locations limit connectivity duration; be prepared to reconnect after periods of inactivity

These environments often optimize for quick customer turnover, which affects how their networks operate.
Overcoming College and University Wi-Fi Restrictions
Educational institution networks implement additional security measures:
- Use institution credentials: Many schools require you to login with your student or faculty ID
- Install security certificates: Some educational networks require installing specific security certificates on your device
- Register your device: Many universities require registering your device’s MAC address before allowing connection
- Use eduroam: If your institution participates in this program, you can use your home institution credentials at partner schools globally
Contact your IT department for institution-specific instructions if these general approaches don’t work.
Security Considerations While Fixing Connection Issues
When troubleshooting, don’t compromise on security.
Safe Password Management Practices
Protect your credentials while troubleshooting:
- Use a password manager: Tools like Bitwarden, LastPass, or 1Password securely store complex Wi-Fi passwords
- Avoid saving passwords on public computers: Never check “remember this network” on shared or public devices
- Create strong, unique passwords: Each network should have its own strong password
- Change default passwords: Always change manufacturer-provided default router passwords
These practices protect your network and devices from unauthorized access during and after troubleshooting.
Protecting Your Data on Troublesome Networks
Stay safe even when desperate for connectivity:
- Use a VPN: Virtual Private Networks encrypt your traffic, protecting it from eavesdropping
- Enable HTTPS Everywhere: This browser extension ensures you’re using encrypted connections when available
- Avoid sensitive transactions: Don’t conduct banking or enter passwords on uncertain networks
- Disable file sharing: Turn off network discovery and file sharing when on public networks
Your security should never be compromised, even when facing connectivity challenges.
Avoiding Common Wi-Fi Security Risks During Troubleshooting
Be alert for these common security pitfalls:
- Watch for network spoofing: Verify you’re connecting to the legitimate network, not a similarly-named impostor
- Check for HTTPS certificates: Look for the padlock icon in your browser and verify site certificates
- Be wary of “free” networks: Unsecured networks with no authentication may be set up to capture your data
- Avoid network “helpers”: Be suspicious of popups offering to “fix” your connection issues
Maintaining security awareness while troubleshooting prevents compounding a connection problem with a security breach.
Local and Regional Wi-Fi Considerations
Network environments vary by region, presenting unique challenges.
Vietnamese-Specific Network Solutions
When troubleshooting in Vietnam, consider these factors:
- Local ISP requirements: Vietnamese providers like VNPT and Viettel may have specific connection procedures
- Popular devices in Vietnam: Oppo, Samsung, and Xiaomi phones dominate the market and may have region-specific firmware
- Public networks: Coffee shops in Vietnam often have password-protected networks with passwords printed on receipts
- Regional regulations: Government regulations may affect network availability and performance
- Vietnamese support resources: Local language support is available through provider hotlines
These considerations help navigate Vietnam’s unique networking environment.
Language and Character Set Issues in Wi-Fi Setup
Character encoding can create unexpected problems:
- Non-ASCII characters in passwords: Some routers struggle with Vietnamese diacritical marks in passwords
- Multilingual interfaces: Router administration pages may display incorrectly if set to an unsupported language
- Font rendering issues: Some devices may display Vietnamese characters incorrectly in network names or credentials
- Input method limitations: Some devices may not support Vietnamese keyboard input for passwords
Using basic Latin characters (A-Z, 0-9) in network names and passwords can avoid these complications.
Supplemental Content: Expert Wi-Fi Connection Insights
When Should You Contact Professional IT Support?
Know when to call in the experts:
- Hardware failure indicators: If your router’s lights behave abnormally or it’s overheating
- Persistent connectivity issues: Problems that remain after trying all standard solutions
- Network-wide problems: Issues affecting all devices, not just one
- Complex network environments: Enterprise networks, mesh systems, or setups with multiple access points
Before calling support, document what you’ve already tried and prepare specific information about your equipment and the problem’s symptoms.
Is Your Wi-Fi Hardware the Real Problem?
Sometimes the issue lies with aging or failing equipment:
- Router age: Devices older than 4-5 years may struggle with modern connection demands
- Signs of hardware failure: Unexplained reboots, overheating, or unusual light patterns
- Interference from new sources: New electronics in your home might interfere with existing equipment
- Capacity limitations: Older routers may not support the number of devices in modern homes
If your troubleshooting points to hardware limitations, upgrading your equipment might be more effective than continued troubleshooting.
How Do Different Wi-Fi Standards Affect Connection Problems?
Understanding Wi-Fi standards can explain compatibility issues:
- 802.11b/g/n (2.4GHz): Older but more compatible standard with better range
- 802.11ac (5GHz): Faster standard but with shorter range and less penetration through walls
- 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6): Newest standard offering better performance in device-dense environments
- Mixed environments: Problems often occur when devices of different generations try to connect
Matching your expectations to your hardware’s capabilities can prevent frustration with older equipment.
What Role Does Your Internet Service Provider Play in Wi-Fi Issues?
Distinguish between local network issues and ISP problems:
- Testing ISP vs. local issues: Connect a computer directly to your modem to determine if the problem is with your Wi-Fi or your internet service
- Checking service status: Most ISPs offer status pages or outage reporting
- Understanding service limitations: Bandwidth caps, throttling, or congestion may affect performance
- Documentation for support calls: Record speed tests, outage times, and error messages before contacting your provider
Having this information ready can make ISP support calls more productive and lead to faster resolutions.
By applying the solutions in this guide, you’ll be able to resolve most Wi-Fi sign-in problems efficiently. Remember that patience and systematic troubleshooting are key—networking issues often require trying several approaches before finding the one that works for your specific situation.

